Cardiac FOCUS - 5 Core View
1. Parasternal Long
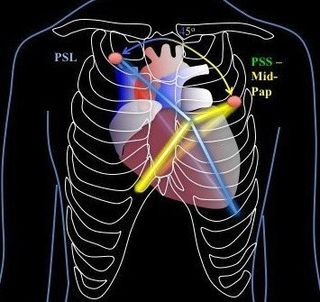
Grip the probe like a pen for this view.
Optimal window is usually attained next to the sternum.
With regards to which intercostal space, it really depends on the patient's anatomy, positioning, and PEEP application though in supine, it can usually be found at around the 3-4th left intercostal space.
Grip the probe like a pen for this view.
Optimal window is usually attained next to the sternum.
With regards to which intercostal space, it really depends on the patient's anatomy, positioning, and PEEP application though in supine, it can usually be found at around the 3-4th left intercostal space.
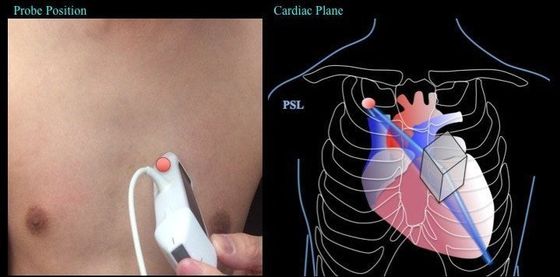
The ultrasound beam is placed along the long axis of the heart -- this is achieved by having the probe's indicator pointing at ~10-11 o'clock. (Turn 45 degrees counter-clockwise from parasternal short).
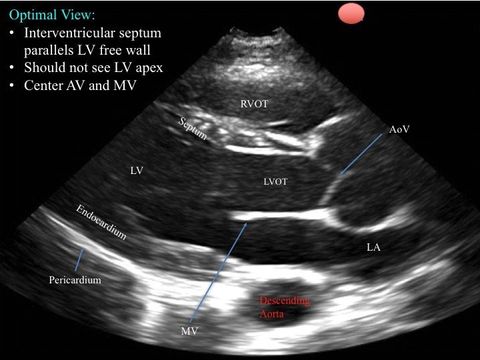
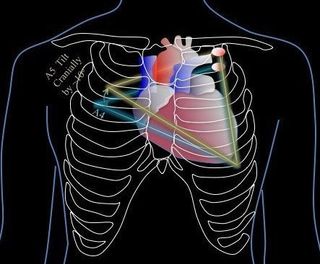
2. Parasternal Short
Grip the probe like a pen.
Optimal window is usually attained next to the sternum.
With regards to which intercostal space, it really depends on the patient's anatomy, positioning, and PEEP application though in supine, it can usually be found at around the 3-4th left intercostal space.
Grip the probe like a pen.
Optimal window is usually attained next to the sternum.
With regards to which intercostal space, it really depends on the patient's anatomy, positioning, and PEEP application though in supine, it can usually be found at around the 3-4th left intercostal space.
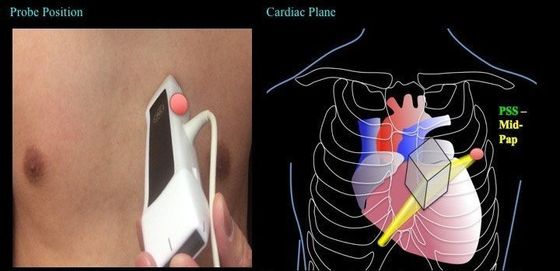
The ultrasound beam is placed along the short axis of the heart -- this is achieved by having the indicator pointing at somewhere ~1-2 o'clock.
(Turn 45 degrees clockwise from parasternal long)
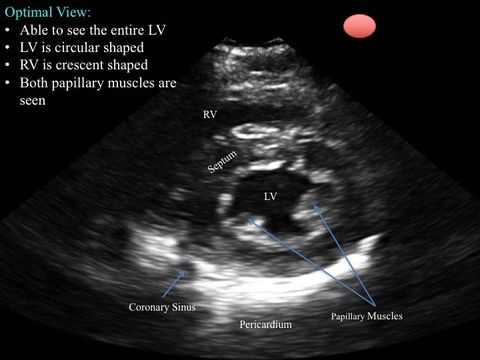
Slide the probe towards the LV apex to find find the papillary muscles (see the image below). Sometimes the optimal view is just one ICS above or inferior; and sometimes the optimal window window is covered by a rib space, so you will have to tilt the probe to attain the view you desire.
Note: the parasternal short has multiple cuts: aortic valve (base of the heart), mitral valve, papillary muscles, and apex.
Slide the probe towards the LV apex to find find the papillary muscles (see the image below). Sometimes the optimal view is just one ICS above or inferior; and sometimes the optimal window window is covered by a rib space, so you will have to tilt the probe to attain the view you desire.
Note: the parasternal short has multiple cuts: aortic valve (base of the heart), mitral valve, papillary muscles, and apex.
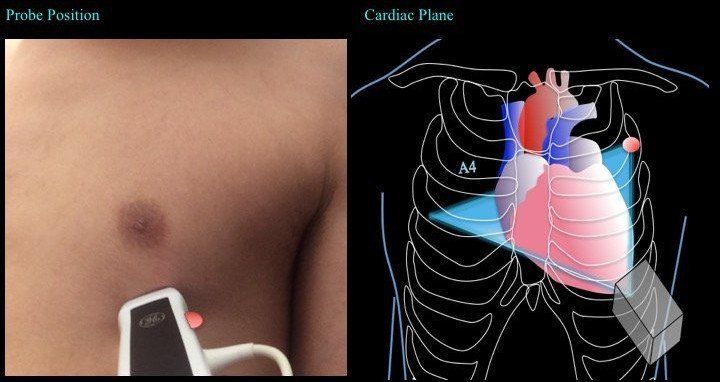
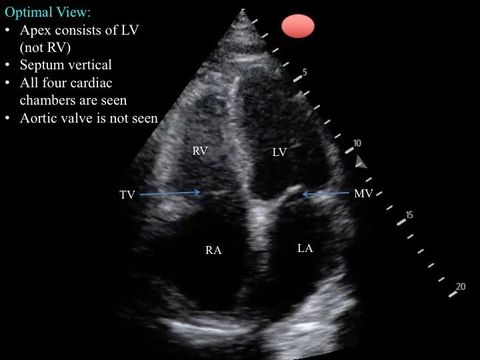
3. Apical 4 Chamber
Use an overhand technique to grip the probe, otherwise, you will not have enough room to tilt the probe.
Place the probe where the apex of the heart is located -- this is the most important step, otherwise, the chambers will be foreshortened. There are several methods to achieve this:
The ultrasound beam is to cut through the heart from the apex at a plane that images the maximal dimension of each chamber.
Troubleshooting:
Use an overhand technique to grip the probe, otherwise, you will not have enough room to tilt the probe.
Place the probe where the apex of the heart is located -- this is the most important step, otherwise, the chambers will be foreshortened. There are several methods to achieve this:
- Place the probe at ~4-5th ICS at the left midclavicular line as a starting point, then adjust.
- Place the probe at ~5th ICS at the left anterior axillary line as a starting point, then interogate medially. If no cardiac motion is found, move the probe to the ICS above at the anterior axillary line and start again.
- Locate the apex via palpation -- where you feel the point of maximal impulse, place the probe there.
- Using parasternal short view, slide (not tilt) the probe until it is imaging the apex.
The ultrasound beam is to cut through the heart from the apex at a plane that images the maximal dimension of each chamber.
Troubleshooting:
- If you are seeing the short and ovoid like ventricles that means your probe is superior to the apex -- fix by sliding your probe laterally or one ICS down.
- If you are seeing the aortic valve, you have attained the apical 5 chamber view. It means that you are cutting the heart at a shallow angle -- correct by tilting the tail of the probe up (away from the chest wall)
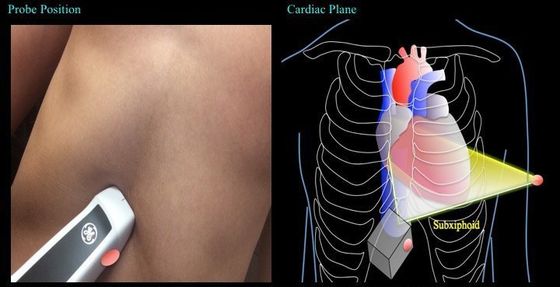
4. Subcostal
Use an over-hand grip for this technique so that there is room for you to lay the probe flat.
First, the probe is placed around the subxiphoid region of the abdomen. Then tilt the tail of the probe towards the abdomen. The probe indicator is pointing at ~3-4 o’clock.
The ultrasound beam is to cut the heart in a similar way per the apical 4 chamber, but this time the beam will originate from the subcostal region.
Use an over-hand grip for this technique so that there is room for you to lay the probe flat.
First, the probe is placed around the subxiphoid region of the abdomen. Then tilt the tail of the probe towards the abdomen. The probe indicator is pointing at ~3-4 o’clock.
The ultrasound beam is to cut the heart in a similar way per the apical 4 chamber, but this time the beam will originate from the subcostal region.
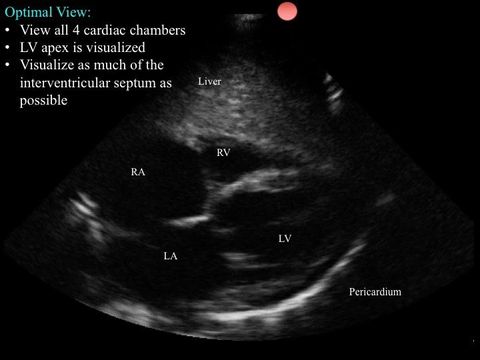
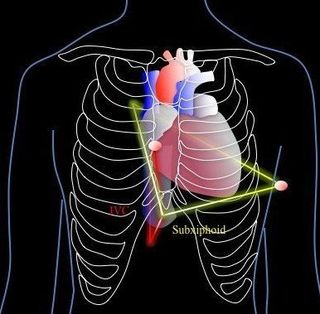
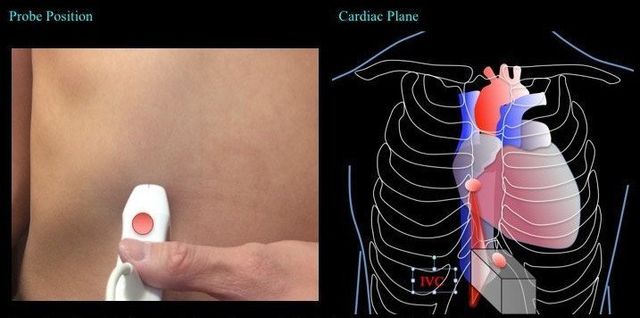
5. Inferior Vena Cava
Grip the probe like a pen.
From the subcostal view, center the right atrium, then rotate the probe counterclockwise by ~90 degrees with the indicator pointing at ~12 o’clock. The tail of the probe is usually pointing upwards -- almost perpendicular to the abdomen.
The ultrasound beam is to cut the IVC long the longitudinal plane.
Grip the probe like a pen.
From the subcostal view, center the right atrium, then rotate the probe counterclockwise by ~90 degrees with the indicator pointing at ~12 o’clock. The tail of the probe is usually pointing upwards -- almost perpendicular to the abdomen.
The ultrasound beam is to cut the IVC long the longitudinal plane.
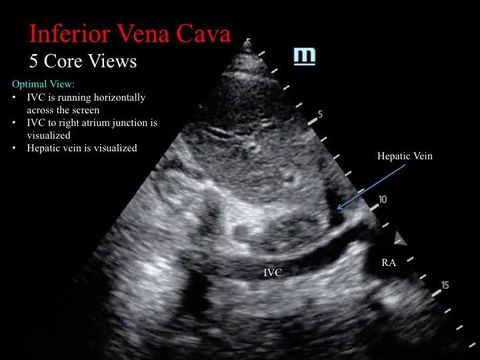
Ensure you are NOT looking at the aorta -- they are close by each other. Often it is falsely visualized as the probe is a bit towards the left of the patient.
Features of IVC:
- thin walled
- surrounded by liver parenchyma on both sides
- drains into RA
- hepatic vein drains into it
Features of Aorta:
- thick wall -- calcification
- liver parenchyma is not around it
- not connected to the RA
Take Home Messages:
- 5 core cardinal views obtained from 3 windows: parasternal, apical, and subcostal views
- PRACTICE, PRACTICE, PRACTICE
- maneuver the patient for an optimal window
- optimize the view